
The if-else statement in C is a flow control statement used for decision-making in the C program. It is one of the core concepts of C programming. It is an extension of the if in C that includes an else block along with the already existing if block.
The if statement in C is used to execute a block of code based on a specified condition.
The syntax of the if statement in C is:
if (condition) < // code to be executed if the condition is true >
The if-else statement is a decision-making statement that is used to decide whether the part of the code will be executed or not based on the specified condition (test expression). If the given condition is true, then the code inside the if block is executed, otherwise the code inside the else block is executed.
if (condition) < // code executed when the condition is true >else < // code executed when the condition is false >
The following program demonstrates how to use if-else in C:
5 is less than 10.
Note: Any non-zero and non-null values are assumed to be true, and zero or null values are assumed to be false.
Working of the if-else statement in C is explained below:

Structure of if-else Syntax in C
We can understand the working of the if-else statement in C with the help of the flowchart.
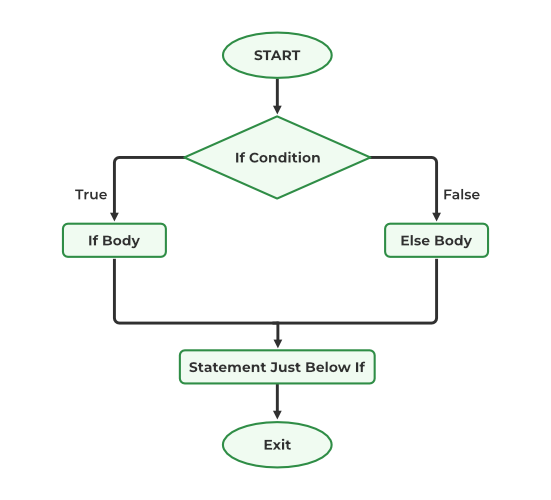
Flowchart of if-else in C
The following are two basic examples of the if-else statement that shows the use of the if-else statement in a C program.
For a given number to be even, it should be perfectly divisible by 2. We will use the if-else statement to check for this condition and execute different statements for when it is true and when it is false.
Number is even
We know that a person is eligible to vote after he/she is at least 18 years old. Now we use this condition in the if-else statement to check the eligibility of the person.
Person 1 is not eligible to vote. Person 2 is eligible to vote.
You may notice that in the second example, we did not enclose the body of the if and else statement in the braces and still the code is running without error. This is because the C language allows the skipping of the braces around the body of the if-else statement when there is only one statement in the body.
In this article, we discussed how to use the if-else statement in C for making decisions in our program based on the specified conditions. Being the core concept of C programming, it is frequently used in almost all C programs.
Answer:
We can skip the braces of the body of the if or else block as long as there is only a single statement inside their body. We will get an error if there is more than one statement in the body without braces.
Answer:
Following is a simple example of the if-else statement in C:
Output
The if block is executed.
Answer:
Answer:
The syntax of the if-else statement is:
if (test expression) < // if body >else < // else body >
The conditional statements (also known as decision control structures) such as if, if else, switch, etc. are used for decision-making purposes in C programs. They are also known as Decision-Making Statements and are used to evaluate one or more conditions and make the decision whether to execute a set of statements or not. These decision-making sta
11 min read Avoiding elif and ELSE IF Ladder and Stairs ProblemThis article focuses on discussing the elif and else if ladder and stairs problem and the solution for the same in the C and Python Programming languages. The ELIF and ELSE IF Ladder and Stairs ProblemThere are programmers who shy away from long sequences of IF, ELSE IF, ELSE IF, ELSE IF , etc. typically ending with a final ELSE clause. In language
6 min read C if else if ladderif else if ladder in C programming is used to test a series of conditions sequentially. Furthermore, if a condition is tested only when all previous if conditions in the if-else ladder are false. If any of the conditional expressions evaluate to be true, the appropriate code block will be executed, and the entire if-else ladder will be terminated.
3 min read Execute both if and else statements in C/C++ simultaneouslyWrite a C/C++ program that executes both if-else block statements simultaneously. Syntax of if-else statement in C/C++ language is: if (Boolean expression) < // Statement will execute only // if Boolean expression is true >else < // Statement will execute only if // the Boolean expression is false >Hence we can conclude that only one of the block
2 min read Print "Even" or "Odd" without using conditional statementWrite a program that accepts a number from the user and prints "Even" if the entered number is even and prints "Odd" if the number is odd. You are not allowed to use any comparison (==, <,>. etc) or conditional statements (if, else, switch, ternary operator,. Etc). Method 1 Below is a tricky code can be used to print "Even" or "Odd" accordi
4 min read Return Statement vs Exit() in main() in C++The return statement in C++ is a keyword used to return the program control from the called function to the calling function. On the other hand, the exit() function in C is a standard library function of <stdlib.h> that is used to terminate the process explicitly. The operation of the two may look different but in the case of the main() funct
3 min read C++ Break StatementThe break in C++ is a loop control statement that is used to terminate the loop. As soon as the break statement is encountered from within a loop, the loop iterations stop there and control returns from the loop immediately to the first statement after the loop. Syntax: break; Basically, break statements are used in situations when we are not sure
5 min read goto Statement in CThe C goto statement is a jump statement which is sometimes also referred to as an unconditional jump statement. The goto statement can be used to jump from anywhere to anywhere within a function. Syntax: Syntax1 | Syntax2 ---------------------------- goto label; | label: . | . . | . . | . label: | goto label; In the above syntax, the first line te
3 min read Break Statement in CThe break statement is one of the four jump statements in the C language. The purpose of the break statement in C is for unconditional exit from the loop What is break in C? The break in C is a loop control statement that breaks out of the loop when encountered. It can be used inside loops or switch statements to bring the control out of the block.
6 min read Return Statement in CPre-requisite: Functions in C C return statement ends the execution of a function and returns the control to the function from where it was called. The return statement may or may not return a value depending upon the return type of the function. For example, int returns an integer value, void returns nothing, etc. In C, we can only return a single
4 min read Continue Statement in CThe continue statement in C is a jump statement that is used to bring the program control to the start of the loop. We can use the continue statement in the while loop, for loop, or do..while loop to alter the normal flow of the program execution. Unlike break, it cannot be used with a C switch case. What is continue in C? The C continue statement
5 min read C - if StatementThe if in C is the most simple decision-making statement. It consists of the test condition and if block or body. If the given condition is true only then the if block will be executed. What is if in C? The if in C is a decision-making statement that is used to execute a block of code based on the value of the given expression. It is one of the cor
5 min read Data type of case labels of switch statement in C++?In C++ switch statement, the expression of each case label must be an integer constant expression. For example, the following program fails in compilation. C/C++ Code /* Using non-const in case label */ #include<stdio.h> int main() < int i = 10; int c = 10; switch(c) < case i: // not a "const int" expression printf("Value of c
2 min read Interesting facts about switch statement in CPrerequisite - Switch Statement in C Switch is a control statement that allows a value to change control of execution. C/C++ Code // Following is a simple program to demonstrate syntax of switch. #include <stdio.h> int main() < int x = 2; switch (x) < case 1: printf("Choice is 1"); break; case 2: printf("Cho
3 min read Implementing ternary operator without any conditional statementHow to implement ternary operator in C++ without using conditional statements.In the following condition: a ? b: c If a is true, b will be executed. Otherwise, c will be executed.We can assume a, b and c as values. 1. Using Binary Operator We can code the equation as : Result = (!!a)*b + (!a)*c In above equation, if a is true, the result will be b.
4 min read Switch Statement in CSwitch case statement evaluates a given expression and based on the evaluated value(matching a certain condition), it executes the statements associated with it. Basically, it is used to perform different actions based on different conditions(cases). Switch case statements follow a selection-control mechanism and allow a value to change control of
8 min read C Programming Language TutorialIn this C Tutorial, you’ll learn all C programming basic to advanced concepts like variables, arrays, pointers, strings, loops, etc. This C Programming Tutorial is designed for both beginners as well as experienced professionals, who’re looking to learn and enhance their knowledge of the C programming language. What is C?C is a general-purpose, pro
8 min read Pattern Programs in CPrinting patterns using C programs has always been an interesting problem domain. We can print different patterns like star patterns, pyramid patterns, Floyd's triangle, Pascal's triangle, etc. in C language. These problems generally require the knowledge of loops and if-else statements. In this article, we will discuss the following example progra
15+ min read C ProgramsTo learn anything effectively, practicing and solving problems is essential. To help you master C programming, we have compiled over 100 C programming examples across various categories, including basic C programs, Fibonacci series, strings, arrays, base conversions, pattern printing, pointers, and more. These C Examples cover a range of questions,
8 min read C Programming Interview Questions (2024)At Bell Labs, Dennis Ritchie developed the C programming language between 1971 and 1973. C is a mid-level structured-oriented programming and general-purpose programming. It is one of the old and most popular programming languages. There are many applications in which C programming language is used, including language compilers, operating systems,
15+ min read C Hello World ProgramThe “Hello World” program is the first step towards learning any programming language and also one of the simplest programs you will learn. To print the "Hello World", we can use the printf function from the stdio.h library that prints the given string on the screen. C Program to Print "Hello World"The following C program displays "Hello World" in
2 min read Dynamic Memory Allocation in C using malloc(), calloc(), free() and realloc()Since C is a structured language, it has some fixed rules for programming. One of them includes changing the size of an array. An array is a collection of items stored at contiguous memory locations. As can be seen, the length (size) of the array above is 9. But what if there is a requirement to change this length (size)? For example, If there is
9 min read Substring in C++The substring function is used for handling string operations like strcat(), append(), etc. It generates a new string with its value initialized to a copy of a sub-string of this object. In C++, the header file which is required for std::substr(), string functions is <string>. The substring function takes two values pos and len as an argument
8 min read Strings in CA String in C programming is a sequence of characters terminated with a null character '\0'. The C String is stored as an array of characters. The difference between a character array and a C string is that the string in C is terminated with a unique character '\0'. C String Declaration SyntaxDeclaring a string in C is as simple as declaring a one-
8 min read Operators in CIn C language, operators are symbols that represent operations to be performed on one or more operands. They are the basic components of the C programming. In this article, we will learn about all the built-in operators in C with examples. What is a C Operator?An operator in C can be defined as the symbol that helps us to perform some specific math
14 min read C PointersPointers are one of the core components of the C programming language. A pointer can be used to store the memory address of other variables, functions, or even other pointers. The use of pointers allows low-level memory access, dynamic memory allocation, and many other functionality in C. In this article, we will discuss C pointers in detail, their
14 min read Data Types in CEach variable in C has an associated data type. It specifies the type of data that the variable can store like integer, character, floating, double, etc. Each data type requires different amounts of memory and has some specific operations which can be performed over it. The data type is a collection of data with values having fixed values, meaning
7 min readArray in C is one of the most used data structures in C programming. It is a simple and fast way of storing multiple values under a single name. In this article, we will study the different aspects of array in C language such as array declaration, definition, initialization, types of arrays, array syntax, advantages and disadvantages, and many more
15+ min read Bitwise Operators in CIn C, the following 6 operators are bitwise operators (also known as bit operators as they work at the bit-level). They are used to perform bitwise operations in C. The & (bitwise AND) in C takes two numbers as operands and does AND on every bit of two numbers. The result of AND is 1 only if both bits are 1. The | (bitwise OR) in C takes two n
7 min read C Language IntroductionC is a procedural programming language initially developed by Dennis Ritchie in the year 1972 at Bell Laboratories of AT&T Labs. It was mainly developed as a system programming language to write the UNIX operating system. The main features of the C language include: General Purpose and PortableLow-level Memory AccessFast SpeedClean SyntaxThese